Installing software in Ubuntu is a piece of cake. Just launch the Ubuntu software center and type in the name of the software in the search bar; click on ‘Install’ and you have it. This all seems and sounds so easy. The part we miss is : there is an Internet connection involved. If you do not have an Internet connection, installing software on Linux machine does not remain easy. In most cases, you cannot simply download a .DEB (or even a .RPM) file and double click to install it! There are a lot of dependencies to be resolved. Unless dependencies are resolved, the software will not behave well. Even it’s running is under question.
However, it is important to understand how to install software on Ubuntu without an internet connection.
Compiling programs from source code
This is the way preferred by geeks because there is no other way which can give more control over software installations. However, it is also complicated because of the technical details involved. If you have never compiled anything, maybe this method is not for you. To follow this method, you must have the source code of the package you want to install. Let us take the example of compiling php on our computer.
- Download the source package. In our case we need to go tohttp://www.php.net/downloads.php and select the package we want. We assume the php-5.3.6.tar.bz2 package is being used for the installtion.
- Now open a shell and go to the directory where the file gets downloaded
- Then unpack the file using the tar command. This will create the required files in the firectory php-5.3.6 and come back to prompt.
- tar -xvf php-5.3.6.tar.bz2 <- Note:please replace the version number with the one you downloaded from the link above.
- Now change the directory to php-5.3.6 by using the cd command. Now run the command.
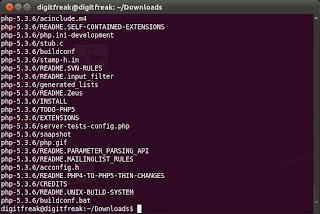
- This will list down the options which the software supports. You can add as many parameters as you want from the list (you should understand what they mean). Once you have done that, run the ./configure script again with the parameters you have selected beofre. Let us assume that we want to enable support for PostgreSQL. Since ./configure –help says :
- –disable-ipv6 Disable Ipv6 support
so we will run the command
- ./configure –disable-ipv6
- The command checks whether the system meets the requirements or not. In the end it throws the error:
- configure: error: xml2-config not found. Please check your libxml2 installation.
Now, we have a problem. This command is a part of the package libxml2-dev. So we have to install that first. Only then shall we be able to compile the php program. Now, this is the most annoying part. The configure script does not report all errors in one go but stops at the first one. If you resolve the first one and then find another, it becomes much difficult.
A bigger problem comes when you are trying to install a dependency (in this case libxml2-dev) and you find that it too needs some other package. Now think of the situation when you hae multiple dependencies (say 7) and each dependency further relies on 4 other dependencies. So there are in total of 28 dependencies which you need to install, one after another. Since, we are talking about installing software on a machine with no Internet con
nection, and it is possible that you might be using the nearest cyber cafe or a friends’ computer to download packages (searching the right version is another problem rooted within this all), it will easily drive you
mad!
However, for sake of simplicity, let us consider for the time being that we have to deal with only one single dependency – libxml2-dev and that we have installed it.
Now run the command again and you should have a long output and the end of it should say “Thank you for using PHP.”
This indicates that the PHP package is ready to be installed .
Note: At this point of time, it has been verified that PHP can be installed on any system because the package was most probably tested by the developers). The only job the configure script does is to check whether the system satisfies the requirements and create other files called ‘makefiles’. A makefile is once again a type of configurationfile. It contains instructions for the compiler.
Now we have to actually compile the package. So call the program ‘make’ by typing the same at the command line. This will call the compiler for every file individually and compile the whole package. Make should produce a lot of output and then get ready with the command line once again. Do notice the last few lines though. If they mention that there was an error then you should ask the community for help (make help). If make did not report error, it’s time to finally install the package. Just say :
Your software should be installed after ‘sudo make install’. But wait do not delete the php-5.3.6 directory. If later on, you want to remove PHP from the machine, you can go back in to the same directory and run ‘sudo make uninstall’ and the software would get removed from your system in an easy way. Otherwise, removing files individually is a real tough challenge, and one with no benefits in almost all cases.
While all this might seem quite easy, the most difficult part of installing software by compilation is where you have to resolve dependencies. It is this part which make the task challenging and geeky. Keeping that part aside, there is almost nothing to be afraid of when it comes to installing software by compilation.
Also, you might be wondering why we are providing with all this extra bit of information and getting you all confused and scared of the steps involved. The main motivation of doing this? We want you to know your Ubuntu better. However at the end it’s you who are going to use it and if you don’t know how Ubuntu works and how to make it do things it’s hard for a user to adopt it. At first it might be look like a little fuss but at the end it’s you who will be benefited the most.